
The Ultimate Guide to Tadalafil
We take a deep dive into all you need to know about tadalafil.

Enclomiphene citrate is scientifically known as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM).
Let’s break down what that means for men. Under normal circumstances, your brain sends a signal to your testes to produce testosterone. Your brain continually monitors your testosterone levels and adjusts your body’s production accordingly.
Persistently low T typically results from one of two different causes: It is usually either the fault of your brain (not sending enough signals to your testes to produce testosterone) or the fault of your testes (failing to produce testosterone despite receiving signals from the brain to do so).
Selective estrogen receptor modulators are a class of medications that increases the signals from your brain to your testes to produce more testosterone.
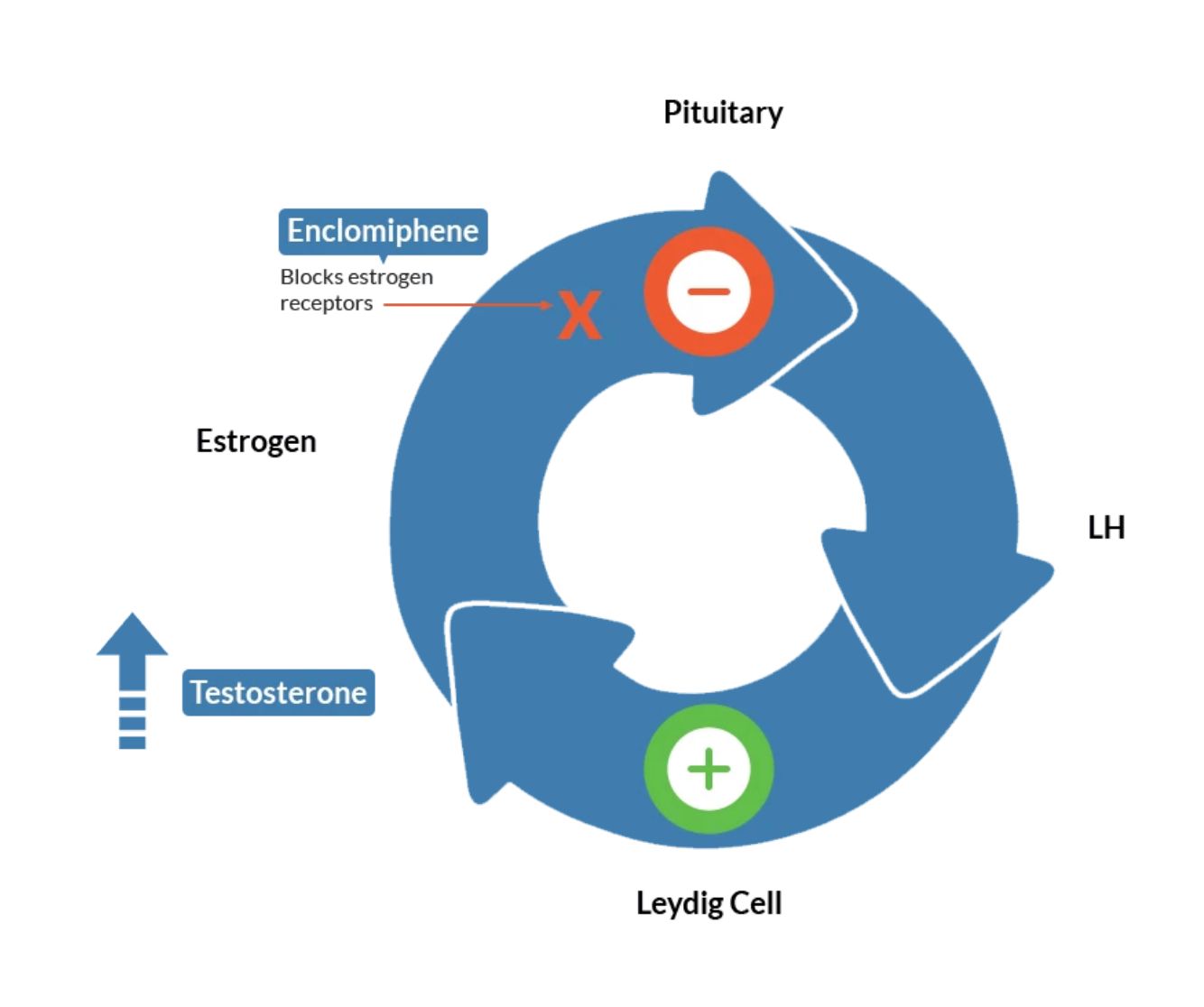
This diagram illustrates how enclomiphene can boost the body’s testosterone levels naturally.
This differs from traditional testosterone replacement therapy (“TRT”), which simply replaces the low testosterone levels in your body by pumping in synthetic testosterone. The problem with this approach is that continued injection of synthetic testosterone can stop the normal processes of testosterone production in your body from occurring. In other words, your brain sends less signals to your testes to produce its own testosterone since it is receiving it from an external source, causing them to become “lazy.”
For example, your testes may begin to shrink because it no longer needs to produce as much testosterone, since you are receiving it from an external source. This is why side effects, such as testicular shrinkage and infertility, are more commonly reported in men who receive testosterone replacement therapy than in those who receive newer therapies such as enclomiphene citrate tablets.
Selective estrogen receptor modulators stimulate your body to produce its own testosterone. In other words, they give the testosterone-producing mechanism in your body a boost.
A study reported, “Enclomiphene citrate is effective in ameliorating testosterone deficiency and maintaining semen quality, with few apparent adverse effects.”
In conclusion, enclomiphene citrate increases testosterone levels safely, without nasty side effects such as testicular shrinkage or infertility.
The primary benefit of enclomiphene citrate is that it raises testosterone levels safely in men who have sub-optimal (less than ideal) T.
Here is a problem that you and I face: studies have found that testosterone levels are declining consistently among men over the last few decades.
According to research, regardless of who you are or what you do, you are likely to have less testosterone than your father or your grandfather did at the same age.
Low T has become a prevalent and unacceptable health threat to men of our generation.
Enclomiphene citrate works by signaling your body to produce more testosterone. It differs from traditional testosterone replacement therapy in that it stimulates your own body to produce testosterone, while testosterone replacement therapy merely replaces it from an external synthetic source.
Most importantly, enclomiphene citrate does this without causing testicular shrinkage and infertility, two common side effects of traditional testosterone replacement therapy.
The benefits of increasing your testosterone levels safely are wide-ranging. It includes:
In other words, because testosterone is involved in the regulation of so many processes in your body, having optimal testosterone levels provides your body with a significant health boost.

Today, studies are showing that American men are facing a silent, mysterious problem that has far-reaching consequences: low levels of testosterone (low T).
A landmark study looking at testosterone levels in men across generations concluded, “The past 20 yr have seen substantial age-independent decreases in male serum T concentrations, decreases that do not appear to be the consequence of the contemporaneous trends in health and lifestyle considered here.”
Let’s break that down. The study concluded that regardless of lifestyle factors (the amount of exercise you do or the kinds of food you eat), men are experiencing a steady drop in testosterone levels over the last few decades.
And this is not dependent on age as well. When matched with men of the same age a few decades ago, statistics show that we as men today have considerably less testosterone.
Which leads us to an alarming reality: men do not have the same testosterone levels as their dads and their granddads.
The study also found, “If the trends observed . . . are real and continue, the prevalence of low T in American men will exhibit increases in excess of those to be expected given the projected aging of the population.”

Source: Pexels / Paul Gray
There are key signs and symptoms of low testosterone, some notable ones that many individuals experience include:
Less of the fuel you need to be the man you were meant to be.
In addition, low T has also been linked to poor mental health, causing problems such as depression and anxiety. If these issues are not dealt with adequately, they can cause a downward spiral that can be difficult to climb out from.
As men, testosterone is vital for most aspects of our health and well-being.
How do we fix the problem of low T?
If men do not have enough testosterone, it makes sense to replace it from an external source, right?
This approach is called testosterone replacement therapy. It is an approach that says that if you have low T, all you need to do is to replace the missing testosterone with synthetic testosterone.
Many men around the world have tried this technique, with mixed results.
The big question here is not whether testosterone replacement therapy is able to replace deficient levels of testosterone, but whether it manages to do so safely.
Studies have demonstrated that traditional testosterone replacement therapy may cause nasty side effects, such as testicular shrinkage and infertility.
Here is what Maximus aims to do: boldly tackle the rising prevalence of low T among modern American men in a way that is both safe and sustainable.
Maximus provides a superior alternative to traditional testosterone replacement therapy with our enclomiphene presciption - an evidence-backed solution for raising testosterone levels without causing testicular shrinkage or infertility.
Enclomiphene citrate is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It works by stimulating your body to produce its own testosterone. This differs from traditional testosterone replacement therapy, which replaces the low testosterone levels in your body by an external source. One of the downsides to traditional testosterone therapy (TRT) is that it can eventually cause your own body to produce less of its own testosterone as it becomes accustomed to receiving it externally.
Maximus believes in empowering men to be the best version of themselves — physically, mentally, and emotionally. By fixing your testosterone levels — a key hormone in men for health and well-being — you are investing in all aspects of your health, giving you the fuel you need to go the distance in life.

Source: Pexels / Victor Freitas
TRT stands for testosterone replacement therapy. For many years, it was (and still is) the default treatment for men with low testosterone levels.
There are many forms of TRT available. For example, a common form of TRT is administered through injecting it into your muscles. Other forms of TRT include patches (that you can stick to your skin) and gels (that you rub into your skin).
TRT, as the name suggests, replaces deficient levels of testosterone with synthetic testosterone from an external source.
Enclomiphene citrate also works by increasing testosterone levels. However, it does so by stimulating your body to produce its own testosterone.
Enclomiphene citrate is taken orally. It does not contain synthetic testosterone.
Scientific evidence suggests that enclomiphene citrate is a safer alternative to TRT in helping you increase your testosterone levels. An unwanted adverse effect of TRT is that it disincentives your body from producing its own testosterone, since it is already receiving testosterone from an external source.
Over time, your body becomes less able to produce testosterone. This can result in testicular shrinkage (since the testes produce testosterone) and infertility.
A study reported, “It is apparent that exogenous testosterone functions as a contraceptive . . . and subsequently may lead to markedly reduced sperm counts in nearly all men.”
This means that testosterone replacement therapy may not be suitable for men who wish to maintain their fertility.
Enclomiphene citrate, however, raises testosterone levels without such problems. A study reported, “Enclomiphene is a very promising drug for patients with secondary hypogonadism [low T due to poor signaling in the body] and who are concerned about the negative effects of exogenous testosterone . . . Ideally, this therapy could become the primary medication for men with secondary hypogonadism who wish to preserve spermatogenesis [the production of sperm].”
The Maximus Testosterone Protocol leverages enclomiphene citrate, the better and safer alternative to increasing your testosterone levels.
Clomid is also known as clomiphene citrate.
As for enclomiphene citrate, scientists wrote, “Enclomiphene represents the purified trans-isomer of clomiphene citrate. Its primary advantage over clomiphene citrate is the absence of the estrogen agonist effects of the cis-isomer, zuclomiphene.”
Let’s break that down. “Trans-isomer”, in simple terms, refers to another form of the same molecule. Imagine yourself looking in the mirror. You and your mirror image are one and the same; the only difference is that when you raise your left hand, your mirror image raises its right.
Clomid contains zuclomiphene, while enclomiphene citrate does not. Zuclomiphene is an estrogen agonist, meaning that it produces effects associated with estrogen, a hormone found in high levels in females compared to males.
Scientists reported that zuclomiphene may have “potential deleterious effects on the male reproductive system.” This is because it inhibits the signals in your body that result in normal testosterone production.
Hence, enclomiphene citrate is a purer form of the medication for the purpose of raising testosterone levels in your body safely.
For a deeper dive, see our guide comparing Clomiphene vs Enclomiphene across safety, efficacy, and more.
hCG refers to human chorionic gonadotropin. hCG is sometimes used to treat low testosterone because it is very similar to a chemical released by the brain to stimulate your testes to produce testosterone. Scientists wrote, “Owing to these structural similarities, hCG is used to stimulate testosterone production.”
Studies have shown that hCG may be useful in treating erectile dysfunction and a lack of sexual desire. It is usually administered via injections twice weekly.
The main disadvantage of hCG treatment is the need for frequent injections, which can cause pain, bruising, and swelling at the injection site. In addition, many studies concerning hCG are conducted on women (to help them ovulate). Hence, scientific data on the use of hCG to increase testosterone is relatively scarce.
Enclomiphene citrate is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It works by increasing the signals in your body to help it produce its own testosterone.
The main advantage of enclomiphene citrate vs hCG is that it is taken orally, which means no nasty injections. In addition, it is also relatively well-researched and found to be relatively safe, with few adverse effects.
Scientists have concluded, “Enclomiphene citrate is effective in increasing serum testosterone levels in hypogonadal men, as well as maintaining sperm counts.”

Source: Pexels / Lukas Medvedevas
Low T is a problem experienced by many men, whether they are aware of it or not. It can cause problems in concentration, sex drive, muscle and bone mass, and overall health.
The best way to buy enclomiphene citrate is through a prescription from a licensed physician who specializes in men’s health. Although enclomiphene citrate is known to have few adverse effects, we highly recommend that you speak to a doctor and get a prescription for enclomiphene citrate before taking it. This is to ensure that you do not have any contraindications that may make you unsuited for this medication.
Although you may be able to find products being marketed as enclomiphene citrate online, there is no guarantee that the drug is real or contains a dosage that is right for you.
At Maximus, we have licensed physicians who specialize in men’s health who will be able to prescribe you the Testosterone Protocol (enclomiphene citrate) if warranted. You can schedule an appointment with one of our doctors via telemedicine. Telemedicine is a doctor’s consultation conducted securely online — think of it like a Zoom call. Your doctor will ask you a few pertinent questions to ensure that the Testosterone Protocol is a good fit for you before prescribing it.
Disclaimer: The contents of this article, including, but not limited to, text, graphics, images, and other information, is for information purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information contained herein is not a substitute for and should never be relied upon for professional medical advice. The content is not meant to be complete or exhaustive or to be applicable to any specific individual's medical condition. You should consult a licensed healthcare professional before starting any health protocol and seek the advice of your physician or other medical professional if you have questions or concerns about a medical condition. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment. Never disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice or treatment because of something you have read on this site. Maximus does not recommend, endorse, or make any representation about the efficacy, appropriateness, or suitability of any specific test, products, procedures, treatments, services, opinions, healthcare providers or other information contained herein. Maximus is not responsible for, nor will they bear any liability for, the content provided herein or any actions or outcomes resulting from or related to its use.
guides